Accounting Equation: a Simple Explanation
Reading time: 6 mins
What is the Accounting Equation?
The Accounting Equation says that Assets are equal to Liabilities plus Equity.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This is a core principle of Accounting. The formula defines the relationship between a business's Assets, Liabilities and Equity. At any moment in time the Accounting Equation must balance. This lays the groundwork for Double-Entry Bookkeeping.
The Accounting Equation is also called:
the Accounting Equation Formula
the Balance Sheet Equation
Basic Accounting Equation
How does the Accounting Equation work?
The Accounting Equation tells us the stuff that a business owns is equal to the stuff that it owes.
Stuff that a business owns = Stuff that a business owes
A business owns Assets and owes Liabilities & Equity. Liabilities are owed to third parties, whereas Equity is owed to the owners of the business.
Which three components make up the Accounting Equation?
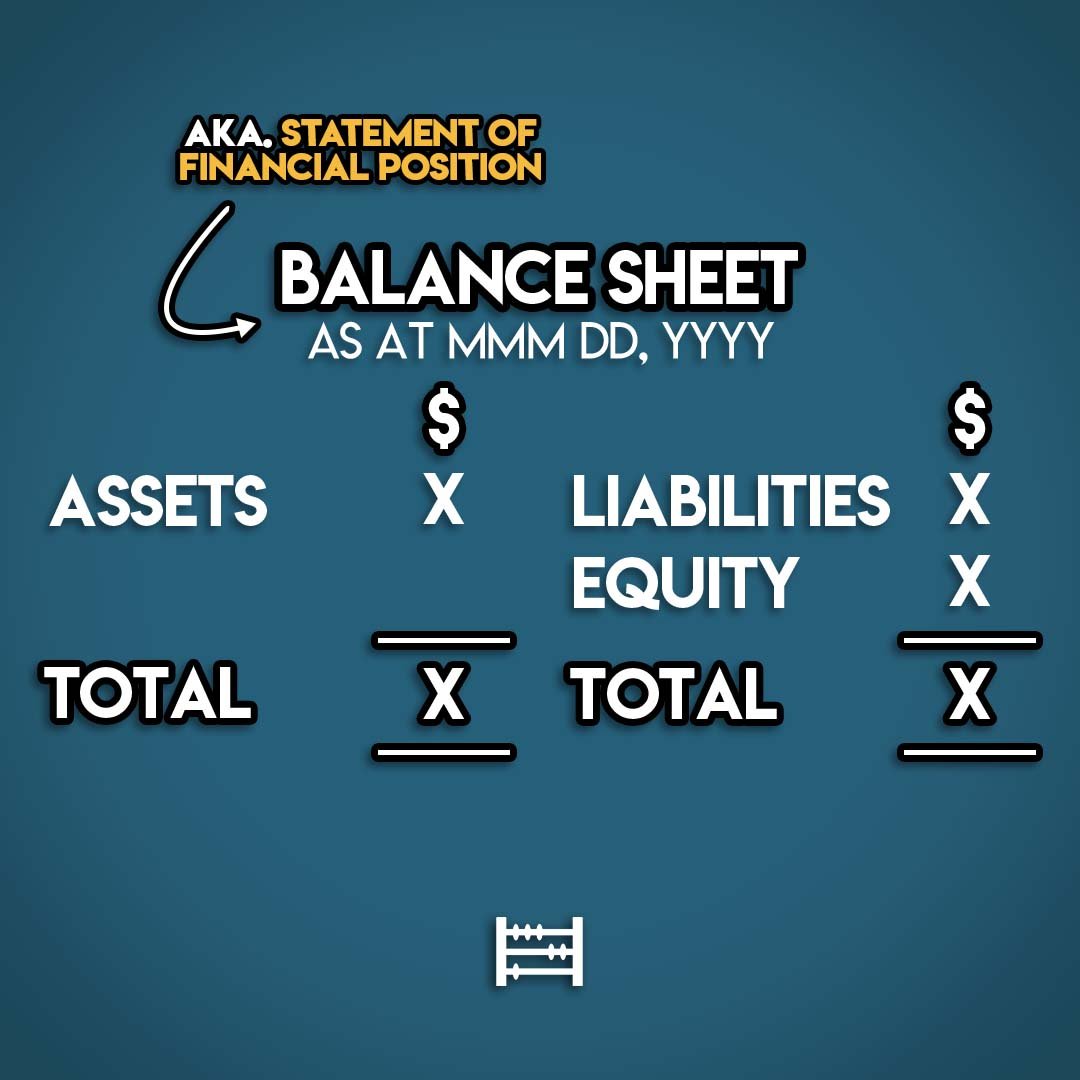
The accounting equation has three components: Assets, Liabilities and Equity. These are broken down on a business's Balance Sheet. The Balance Sheet is a Financial Statement that gives us a snapshot of a business's Assets, Liabilities and Equity at a point in time.
Let's take a closer look at each of these elements so that we can understand them better.
Assets
Assets are the stuff that a business owns that have value. They make up one side of the Accounting Equation. You can think of them as resources that a business controls due to past transactions or events. Assets can be current or non-current.
Current Assets
Current Assets are Short-Term Assets. These are expected to be converted into cash in under one year. They include:
Cash
Short-Term Investments
Accounts Receivable
Inventory
Accrued Revenue
Prepaid Expenses
Non-Current Assets
Non-Current Assets are Long-Term Assets. These aren't as easy to convert into cash. They are expected to be held for more than one year. They are made up of:
Long-Term Investments
Property, Plant & Equipment
Intangible Assets
Liabilities
Liabilities are the stuff that a business owes to third parties. Along with Equity, they make up the other side of the Accounting Equation. Liabilities are a business' obligations to third parties. They require a sacrifice of economic benefit in the future. Liabilities can also be Current or Non-Current.
Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities are Short-Term Liabilities. These are a business's obligations that need to be settled within one year. They include:
Accounts Payable
Salaries Payable
Taxes Payable
Accrued Expenses
Deferred Revenue
Short-Term Debt
Non-Current Liabilities
Non-Current Liabilities are Long-Term Liabilities. These are obligations that aren't expected to be settled within one year. These are some common examples of Long-Term Liabilities:
Long-Term Debt
Notes Payable
Equity
Equity is the stuff that a business owes to its owners. If we rearrange the Accounting Equation, Equity is equal to Assets minus Liabilities. Net Assets is the term used to describe Assets minus Liabilities.
Equity = Assets - Liabilities = Net Assets
So Equity is the owner's claim on the Net Assets of a business. It's made up of:
Capital Contributions
Retained Earnings
Accounting Equation Example
Let me show you how the Accounting Equation works with an example.
Storyteller's Corner is a bookstore. On December 31st, 20X5 they reported the following numbers on their Balance Sheet:
Total Assets: $100,000
Total Liabilities: $70,000
Total Equity: $30,000
On the left side of the Accounting Equation Storyteller's Corner has Total Assets of $100,000. On the right, they have Total Liabilities of $70,000 and Total Equity of $30,000. This adds up to $100,000 ($70,000 + $30,000). This matches their Total Assets on the left of the Accounting Equation.
Total Assets = Total Liabilities + Total Equity
What is Double-Entry Accounting?
In Double-Entry Accounting, there are at least two sides to every financial transaction. Every accounting entry has an opposite corresponding entry in a different account. This principle ensures that the Accounting Equation stays balanced.
For example, imagine that a business's Total Assets increased by $500. This change must be offset by a $500 increase in Total Liabilities or Total Equity.
Debits and Credits are the words used to reflect this double-sided nature of financial transactions.
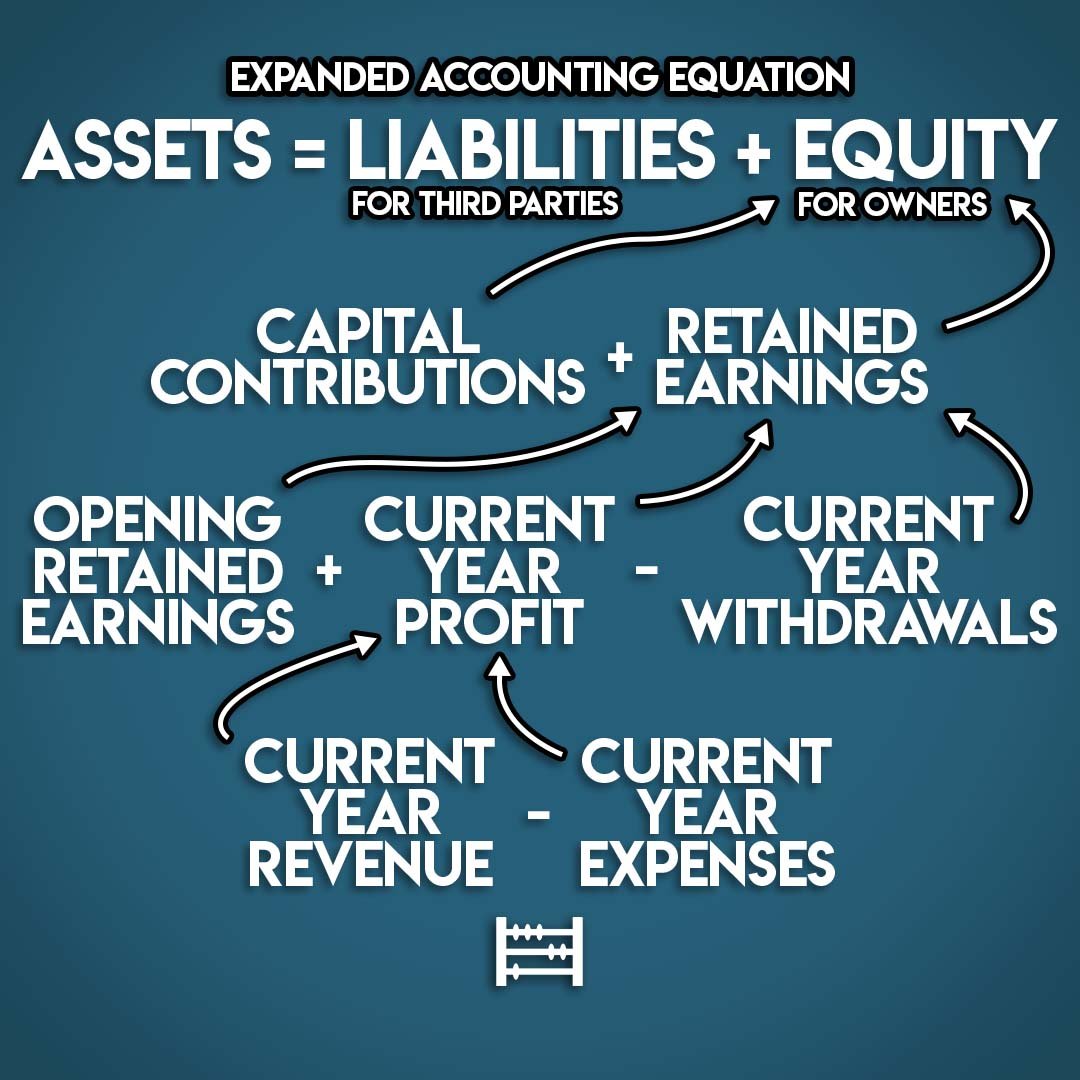
What is the Expanded Accounting Equation?
The Expanded Accounting Equation breaks Equity down into its core components. These include:
Capital Contributions: Funds invested into the business out of the owner's own pocket.
Opening Retained Earnings: Profits held for future use at the start of the accounting period.
Revenue: Income earned during the current year
Expenses: Costs incurred during the current year
Withdrawals: Earnings distributions the business owners during the current year
The Expanded Accounting Equation is:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital Contributions + Opening Retained Earnings + Revenue - Expenses - Withdrawals
This is the same as the Basic Accounting Equation but it contains more detail on the sources of Equity.
Key Points
The basic Accounting Equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Assets are the stuff that a business owns that have value.
Liabilities are the stuff that a business owes to third parties.
Equity is the owner's claim on the Net Assets of a business.
A Balance Sheet is a snapshot of the Accounting Equation at a point in time.
This formula is the backbone of Double-Entry Accounting.
The Expanded Accounting Equation breaks Equity down into its core components.
More Accounting Equation Resources
Free Accounting Equation Cheat Sheet
I have summarized all this information in my Accounting Equation Cheat Sheet.
You can download it here for free:
Accounting Equation Video
In this short video I summarize how the Accounting Equation works:
Accounting Equation Practice Questions
You can test your understanding of the Accounting Equation in this short quiz:
I have also made an Accounting Equation Practice Question Pack which you can buy here: